Eukaryotic cells may contain all of the following EXCEPT. The nuclear membrane is continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum.
Focus On Eukaryotic Cells Springerlink
In this article we will mainly cover animal and plant cells.

. What is an example of a testcross. Chloroplast is surrounded by two unit membranes. What are the domains.
The boundary of the nucleus is called the nuclear envelope. A typical cell contain which of the following main components. The mitochondrial matrix 4.
A typical photosynthetic eukaryotic cell contains which of the following I from BIOL 1350 at University of Colorado Colorado Springs. Which of the following membranes or compartments can be found in both a cyanobacterial cell and a typical photosynthetic eukaryotic cell. Which of the following statements about algae and fungi is are true.
A eukaryotic cell is a compartmentalised cell that contains organelles such as a nucleus and mitochondria. A a membrane-bounded nucleus b a cell wall made of cellulose c ribosomes d flagella or cilia that contain microtubules e linear chromosomes made of DNA and protein 2. X aa used to determine an organisms genotype.
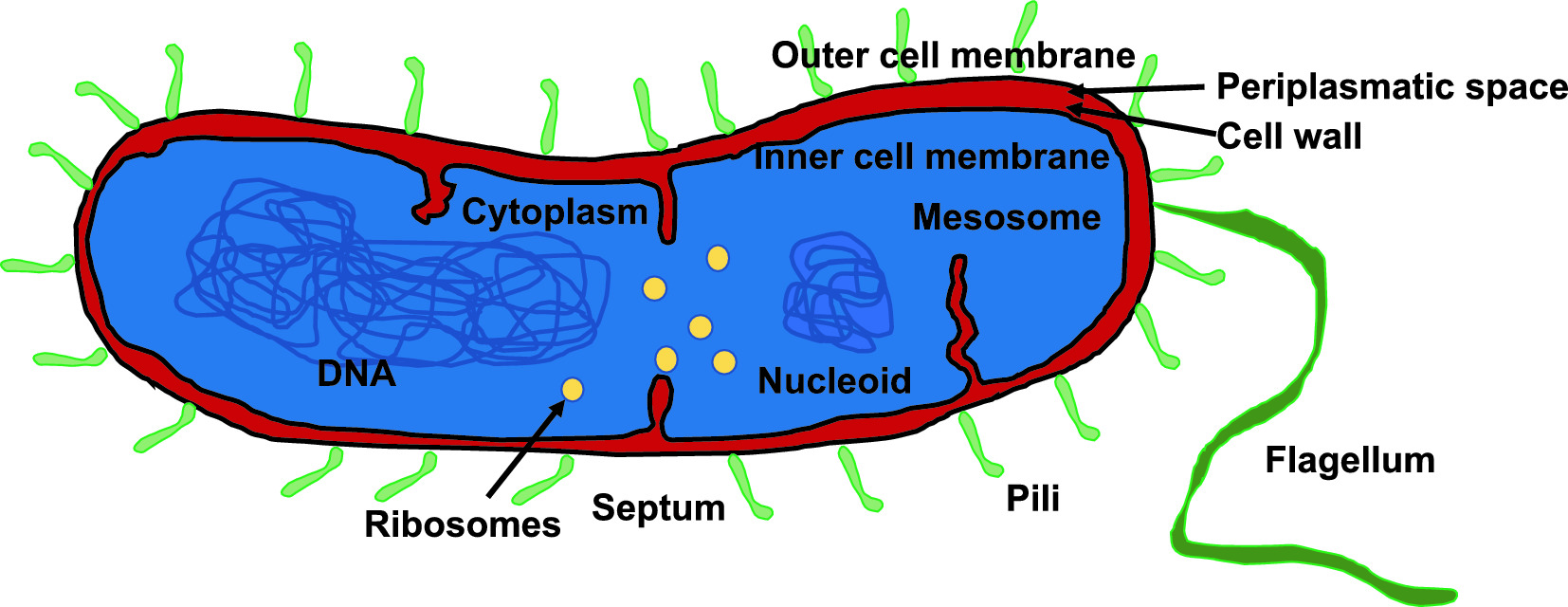
A typical photosynthetic eukaryotic cell contains which of the following. An outer membrane and an inner membrane. The thylakoid membrane Prokaryotic cells are cells without a nucleus.
It consists of two phospholipid bilayers. - Photosynthesis Select that statement that reflects evidence that directly supports the endosymbiotic theory. A Monera b Animalia c Plantae d Fungi a Monera.
Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. The inner mitochondrial membrane 5. The glycocalyx of a eukaryotic cell is - Mostly polysaccharides.
Correct option is C Prokaryotes lack an organized nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. - The electron transport system is located in the cell membrane in bacteria while in eukaryotes it is located in the mitochondrial cristae. The outer mitochondrial membrane 3.
In a testcross the individual with the unknown genotype is crossed with a homozygous recessive individual. Solution for eukaryotic cells which of the following is typical of how transcription is regulated. A Algae are photosynthetic whereas fungi are not b Algal cell walls contain cellulose whereas fungal cell walls do not c Fungal cell walls contain chitin whereas algal cell walls do not d All of the above.
All of the above. Although plastids probably had a single. It is the familiar type of plastid containing photosynthetic pigment the chlorophyll.
A typical photosynthetic eukaryotic cell contains which of the following I from ECON 101 at Western Michigan University. Prokaryotes are classified as belonging to two different domains. Fungal Cells The cell wall is made of chitin.
Group of answer choices Activators and enhancers at sites. There are four main types of eukaryotic cells. Some fungi have holes known as septa which allow the organelles and cytoplasm to pass through them.
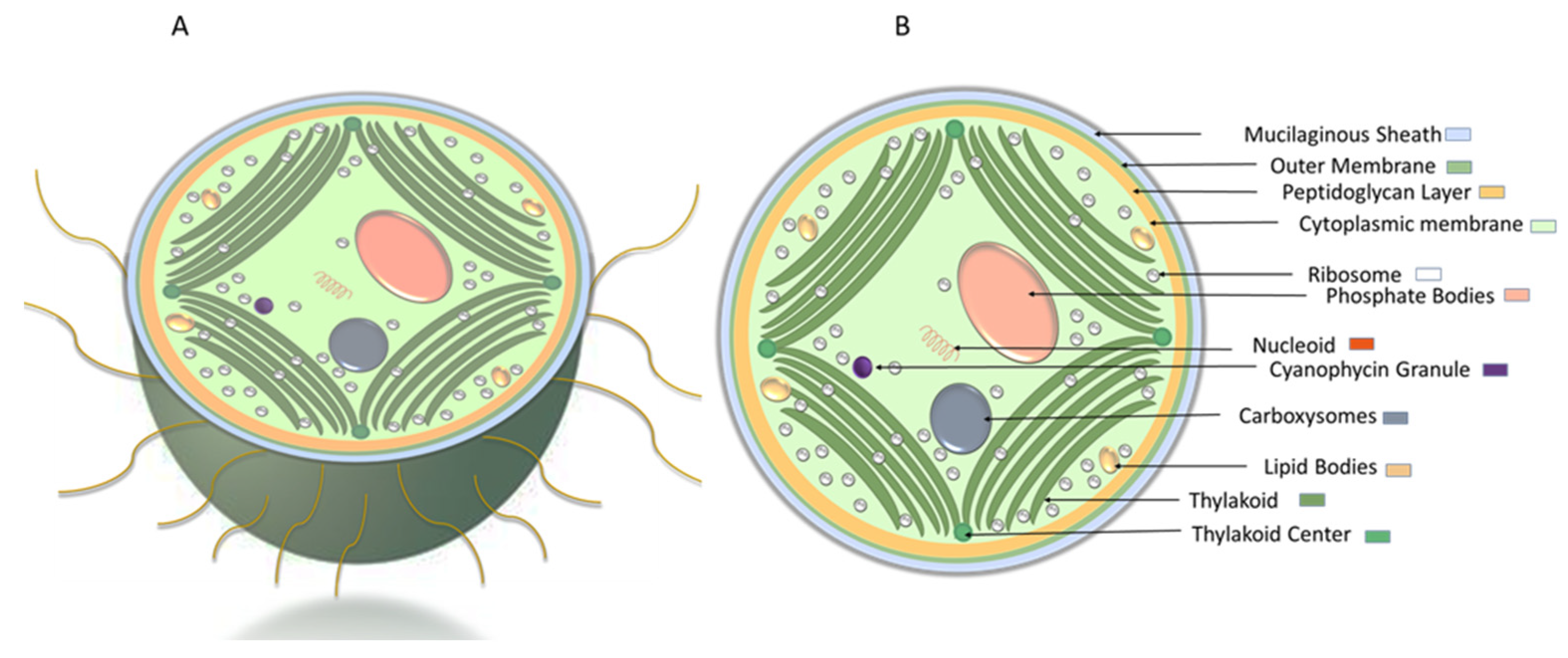
They usually take the form of chloroplasts which like cyanobacteria contain chlorophyll and produce organic compounds such as glucose through photosynthesis. They act as storage for reserve material in prokaryotic cells. Special gas storing vacuoles are seen in cyanobacteria and other photosynthetic bacteria.
Plant animal fungi and protist cells. The plant cell contains chloroplast which aids in the process of photosynthesis. Instead they have a cell membrane.
They exist freely in the cytoplasm without a membrane. Prokaryotic DNA is found in a central part of the cell called the nucleoid. Others are involved in storing food.
Flagella Some bacteria have extensions coming from their cell wall called flagella that help them move. A peptidoglycan cell. Fungi archaea viruses bacteria protists fungi and protists Select all the correct statements regarding the size of different microbes Some eukaryotic microbes are smaller than many bacteria and archaea.
Start studying Clep 2. The cell wall of the prokaryote acts as an extra layer of protection that helps maintain cell. Animal Cells These do not have cell walls.
The cell membrane also called plasma membrane Cytoplasm. The nucleolus is a condensed region of chromatin where ribosome synthesis occurs. The photosynthetic prokaryote eventuallyover evolutionary timebecame __________.
The inner nuclear membrane 2. Correct option is D Be it a plant cell or an animal cell three essential parts are observed under the microscope. Chloroplasts Eukaryotic cells are not found in which of the following kingdoms.
Some of these new cells engaged in a second merging event with a photosynthetic prokaryote possibly a cyanobacterium. Mitochondria I II and III. Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells generally have which of the following features in common.
The internal structure shows the colourless ground substance called stroma in which dark reaction occurs and closed flat sac like membrane system called grana where light reaction photochemical occurs. Some bacteria and archaea are larger than the largest known protists. Open in App.
Unlike prokaryotes which do not have a nucleus all eukaryotes have a nucleus. Most eukaryotic cells are alrger than msot bacterial and archaeal cells. That is why animals have varied shapes.

We Are Aware That All Life Stems From A Single Cell And That The Cell Is The Most Basic Unit Of All Living Organism Plant Cell Diagram Cell Diagram Plant Cell
Microorganisms Free Full Text Cyanobacteria Model Microorganisms And Beyond Html

0 Comments